맥OS에서 Homebrew를 통해 도커를 설치할 수 있다. brew와 brew cask를 통해 설치할 수 있는데, 두 방법에는 차이가 있어 기록한다.
Homebrew 설치 두가지 방법
Homebrew를 통해 도커를 설치하는 방법은 두 가지가 있다. brew와 brew cask를 통해 설치할 수 있다.
brew cask는 Docker Desktop on Mac 도커를 설치해주며, docker-compose, docker-machine을 같이 설치해준다.
그리고 맥OS에서 띄우는 것이기 때문에 서버를 띄웠을 때, 가상 머신에서 포트 포워딩할 필요가 없다.
brew를 통해 설치할 경우 virtualbox, vargrant 등 가상머신 위에 도커를 띄우는 작업을 해야한다.
그리고 brew cask와 다르게 compose, machine 등 필요한 것들을 추가 설치할 필요가 있다.
또 서버를 실행했을 때 호스트OS에서 서버에 접근하려면 포트포워딩 설정을 해줘야한다.
개인적으로 맥에서 사용할때는 Docker Desktop on Mac을 더 선호한다.
brew cask install
1 | |
설치하면 Applications 디렉토리에 docker.app이 있는 걸 확인할 수 있다. 이를 실행해주면 시스템바에 귀여운 도커 아이콘이 생긴다. (괜히 귀엽다)
(한번 실행해줘야 /usr/local/bin에 도커 링크가 생기고, 터미널에서 작업할 수 있다)
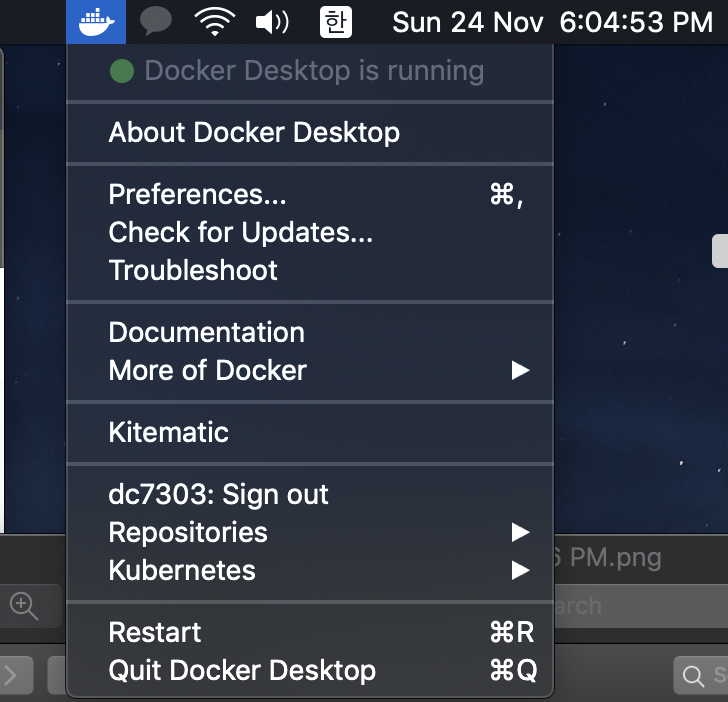 <도커가 실행된 모습>
<도커가 실행된 모습>
그리고 터미널에서 실행해보자.
1 | |
brew install
도커, 가상머신 설치
1 | |
여기서 virtualbox를 설치할 때 아래 이미지와 같은 에러로 실패하는 걸 확인할 수 있다.
 <버츄얼박스 설치 에러>
<버츄얼박스 설치 에러>
이때 System Preferences -> Security & Privacy 메뉴에 접근하면 아래 이미지와 같은 메세지가 나올 것이다.
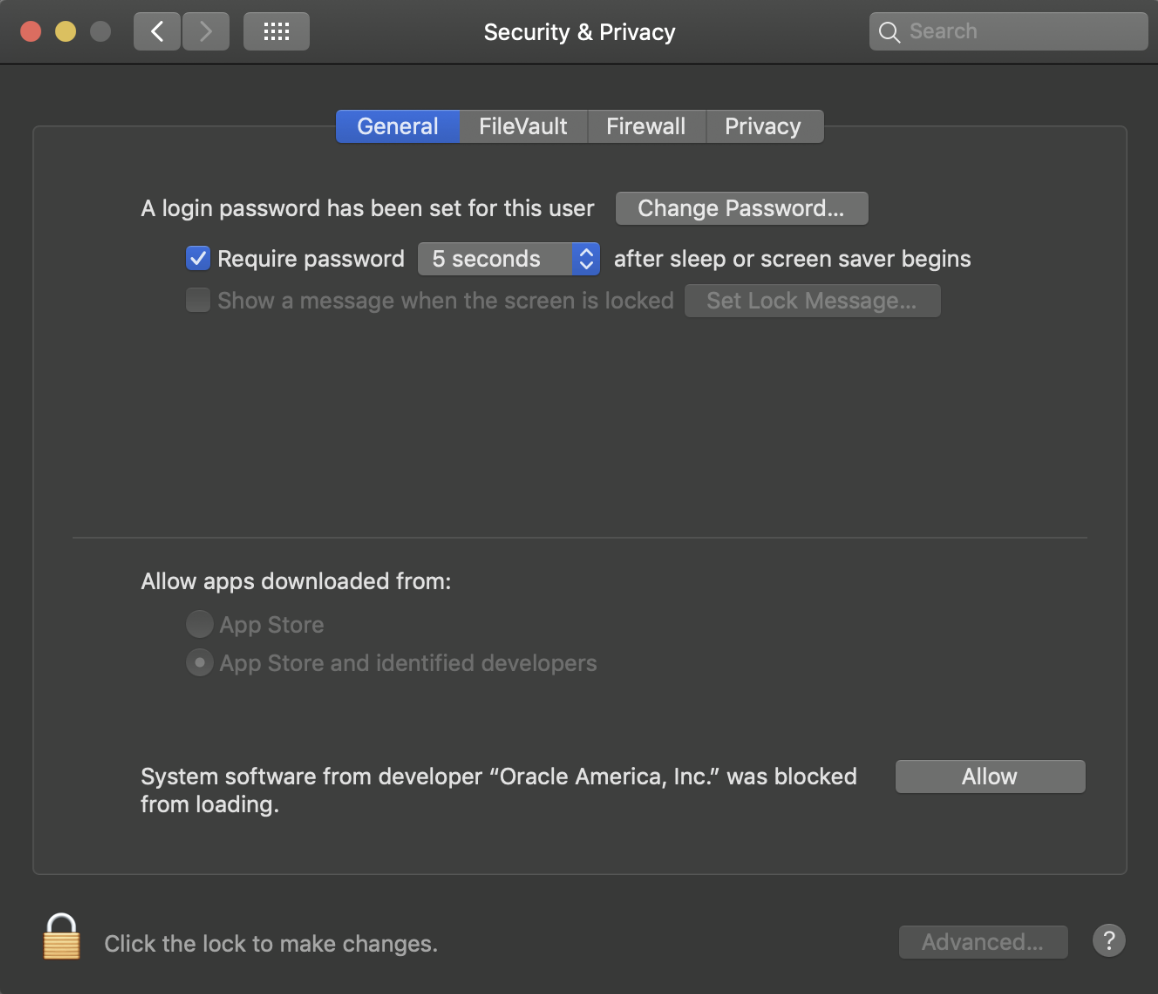 <Security & Privacy>
<Security & Privacy>
Allow 해주고 다시 brew cask install virtualbox를 실행해주면 설치가 완료된다.
가상 머신 생성 및 설정
docker-machine을 통해 가상 머신을 생성한다.
1 | |
가상 머신을 생성했으면, 도커 명령을 사용할 시스템을 설정한다.
1 | |
이 작업은 쉘 설정 파일에서 자동화할 수 있다.
1 | |
정상적으로 동작하는지 확인해보자.
1 | |